级联操作有哪些?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| package javax.persistence;
public enum CascadeType {
/** Cascade all operations */
ALL,
/** Cascade persist operation */
PERSIST,
/** Cascade merge operation */
MERGE,
/** Cascade remove operation */
REMOVE,
/** Cascade refresh operation */
REFRESH,
/**
* Cascade detach operation
*
* @since 2.0
*
*/
DETACH
}
|
测试环境
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author itning
* @date 2020/3/26 12:06
*/
@Entity
@Data
public class Father {
@Id
private String id;
@Column
private String name;
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.PERSIST)
@JoinColumn(name = "father_id")
List<Son> sons;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
/**
* @author itning
* @date 2020/3/26 12:07
*/
@Data
@Entity
public class Son {
@Id
private String sonId;
@Column
private String sonName;
@ManyToOne
private Father father;
public Son(String sonId, String sonName) {
this.sonId = sonId;
this.sonName = sonName;
}
public Son() {
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import top.itning.springboottest.entity.Father;
/**
* @author itning
* @date 2020/3/26 12:22
*/
public interface FatherRepository extends JpaRepository<Father, String> {
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import top.itning.springboottest.entity.Son;
/**
* @author itning
* @date 2020/3/26 12:23
*/
public interface SonRepository extends JpaRepository<Son, String> {
}
|
ALL
这个会所有情况下均进行关联操作,即save-update和delete
PERSIST(级联持久化)
将Father类中sons属性的注解改成@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.PERSIST)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Test
public void test() {
ArrayList<Son> sons = Lists.newArrayList(
new Son("sa", "sa"),
new Son("sb", "sb")
);
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
father.setName("a");
father.setSons(sons);
fatherRepository.save(father);
}
|
测试运行后,会抛出异常
1
| Caused by: javax.persistence.EntityNotFoundException: Unable to find top.itning.springboottest.entity.Son with id sa
|
可知:级联持久化时,JPA不会新增保存外键
将外键对象注释,重新测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Test
public void test() {
/*ArrayList<Son> sons = Lists.newArrayList(
new Son("sa", "sa"),
new Son("sb", "sb")
);*/
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
father.setName("a");
//father.setSons(sons);
fatherRepository.save(father);
}
|
正常保存Father,SQL如下:
1
2
| select father0_.id as id1_0_0_, father0_.name as name2_0_0_ from father father0_ where father0_.id=?
insert into father (name, id) values (?, ?)
|
这时,我们写入Son表两条数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @Test
public void test2() {
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
Son son = new Son();
son.setSonId("sa");
son.setSonName("sa");
son.setFather(father);
Son son2 = new Son();
son2.setSonId("sb");
son2.setSonName("sb");
son2.setFather(father);
sonRepository.save(son);
sonRepository.save(son2);
}
|
取消注释并重新执行刚才出现异常的测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Test
public void test() {
ArrayList<Son> sons = Lists.newArrayList(
new Son("sa", "sa1"),
new Son("sb", "sb1")
);
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
father.setName("b");
father.setSons(sons);
fatherRepository.save(father);
}
|
注意:我们把Son对象的sonName属性值全部增加了1,father.setName("b");
测试输出的SQL:
1
2
3
| select father0_.id as id1_0_0_, father0_.name as name2_0_0_ from father father0_ where father0_.id=?
select sons0_.father_id as father_i3_1_0_, sons0_.son_id as son_id1_1_0_, sons0_.son_id as son_id1_1_1_, sons0_.father_id as father_i3_1_1_, sons0_.son_name as son_name2_1_1_ from son sons0_ where sons0_.father_id=?
update father set name=? where id=?
|
只发送的两条查询SQL和一条更新Father的SQL,并没有将Son表的值进行更改。
接下来看下删除:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testDel() {
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
fatherRepository.delete(father);
}
|
测试输出SQL:
1
2
3
| select father0_.id as id1_0_0_, father0_.name as name2_0_0_ from father father0_ where father0_.id=?
update son set father_id=null where father_id=?
delete from father where id=?
|
可以看到,只会将father删除,不会删除son而会将其外键设为null
总结
- 级联持久化新增时不会将外键对象保存
- 级联持久化更新时不会更新外键对象
- 级联持久化删除时不会删除外键对象
我们刚才把CascadeType.PERSIST放在了father类中,我们这回放在son中试试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
/**
* @author itning
* @date 2020/3/26 12:07
*/
@Data
@Entity
public class Son {
@Id
private String sonId;
@Column
private String sonName;
@ManyToOne(cascade = CascadeType.PERSIST)
private Father father;
public Son(String sonId, String sonName) {
this.sonId = sonId;
this.sonName = sonName;
}
public Son() {
}
}
|
依照刚才的测试,结果没有区别
MERGE(级联更新(合并))
将所有更改重置,并将father类更改如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author itning
* @date 2020/3/26 12:06
*/
@Entity
@Data
public class Father {
@Id
private String id;
@Column
private String name;
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.MERGE)
@JoinColumn(name = "father_id")
List<Son> sons;
}
|
运行以下测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Test
public void test() {
ArrayList<Son> sons = Lists.newArrayList(
new Son("sa", "sa"),
new Son("sb", "sb")
);
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
father.setName("a");
father.setSons(sons);
fatherRepository.save(father);
}
|
看到执行的SQL:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| select father0_.id as id1_0_1_, father0_.name as name2_0_1_, sons1_.father_id as father_i3_1_3_, sons1_.son_id as son_id1_1_3_, sons1_.son_id as son_id1_1_0_, sons1_.father_id as father_i3_1_0_, sons1_.son_name as son_name2_1_0_ from father father0_ left outer join son sons1_ on father0_.id=sons1_.father_id where father0_.id=?
select son0_.son_id as son_id1_1_0_, son0_.father_id as father_i3_1_0_, son0_.son_name as son_name2_1_0_ from son son0_ where son0_.son_id=?
select son0_.son_id as son_id1_1_0_, son0_.father_id as father_i3_1_0_, son0_.son_name as son_name2_1_0_ from son son0_ where son0_.son_id=?
insert into father (name, id) values (?, ?)
insert into son (father_id, son_name, son_id) values (?, ?, ?)
insert into son (father_id, son_name, son_id) values (?, ?, ?)
update son set father_id=? where son_id=?
update son set father_id=? where son_id=?
|
可以看到不仅保存了father,还保存了son
我们更新下试试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Test
public void test() {
ArrayList<Son> sons = Lists.newArrayList(
new Son("sa", "sa2"),
new Son("sb", "sb2")
);
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
father.setName("a");
father.setSons(sons);
fatherRepository.save(father);
}
|
将Son的sonName全加个2
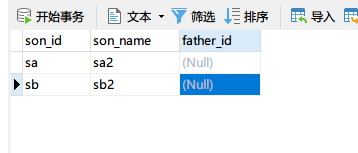
执行后正常修改了sonName,但是把外键设置成了null了
我们修改下测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Test
public void test() {
Father f = new Father();
f.setId("a");
ArrayList<Son> sons = Lists.newArrayList(
new Son("sa", "sa2", f),
new Son("sb", "sb2", f)
);
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
father.setName("a");
father.setSons(sons);
fatherRepository.save(father);
}
|
这个时候son表的外键就不是null啦
接下来测试删除:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testDel() {
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
fatherRepository.delete(father);
}
|
执行的SQL:
1
2
3
| select father0_.id as id1_0_0_, father0_.name as name2_0_0_ from father father0_ where father0_.id=?
update son set father_id=null where father_id=?
delete from father where id=?
|
可以看到,并没有删除son而只是把其外键设置为null了
总结
- 级联更新保存时会保存所有
- 级联更新时会更新所有
- 级联删除时不会删除多的那方
将CascadeType.MERGE放在Son的情况有所不同:
新增father不会新增son,而是会抛出异常
新增son会将father一并新增,但是son中外键为null,想不为null需要设置father.setSons(sons);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| @Test
public void test2() {
Father father = new Father
father.setId("a");
father.setName("a");
Son son = new Son();
son.setSonId("sa");
son.setSonName("sa");
son.setFather(father);
Son son2 = new Son();
son2.setSonId("sb");
son2.setSonName("sb");
son2.setFather(father);
sonRepository.save(son);
sonRepository.save(son2);
}
|
更新son也会将father进行更新
删除son也时仅仅删除son不会动father
REMOVE(级联删除)
将所有更改重置,并将father类更改如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author itning
* @date 2020/3/26 12:06
*/
@Entity
@Data
public class Father {
@Id
private String id;
@Column
private String name;
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.REMOVE)
@JoinColumn(name = "father_id")
List<Son> sons;
}
|
运行以下测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Test
public void test() {
ArrayList<Son> sons = Lists.newArrayList(
new Son("sa", "sa"),
new Son("sb", "sb")
);
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
father.setName("a");
father.setSons(sons);
fatherRepository.save(father);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @Test
public void test2() {
Father father = new Father()
father.setId("a");
Son son = new Son();
son.setSonId("sa");
son.setSonName("sa");
son.setFather(father);
Son son2 = new Son();
son2.setSonId("sb");
son2.setSonName("sb");
son2.setFather(father);
sonRepository.save(son);
sonRepository.save(son2);
}
|
以上两个测试用例都会抛出错误。
所以级联删除不会保存外键对象
接下来,我们正常添加数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| @Test
public void test2() {
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
father.setName("a");
fatherRepository.save(father);
Son son = new Son();
son.setSonId("sa");
son.setSonName("sa");
son.setFather(father);
Son son2 = new Son();
son2.setSonId("sb");
son2.setSonName("sb");
son2.setFather(father);
sonRepository.save(son);
sonRepository.save(son2);
}
|
测试下更新时会不会更新关联表:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Test
public void test() {
ArrayList<Son> sons = Lists.newArrayList(
new Son("sa", "sa2"),
new Son("sb", "sb2")
);
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
father.setName("a");
father.setSons(sons);
fatherRepository.save(father);
}
|
测试发出了两条查询SQL,并没有更新语句
所以级联删除不会更新关联表
接下来测试下删除:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testDel() {
Father father = new Father();
father.setId("a");
fatherRepository.delete(father);
}
|
这样仅仅删除了father并不会删除son
想要也删除son表:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author itning
* @date 2020/3/26 12:06
*/
@Entity
@Data
public class Father {
@Id
private String id;
@Column
private String name;
@OneToMany(cascade = {CascadeType.REMOVE}, mappedBy = "father")
List<Son> sons;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.*;
/**
* @author itning
* @date 2020/3/26 12:07
*/
@Data
@Entity
public class Son {
@Id
private String sonId;
@Column
private String sonName;
@ManyToOne(optional = false)
@JoinColumn(name = "father_id")
private Father father;
public Son(String sonId, String sonName) {
this.sonId = sonId;
this.sonName = sonName;
}
public Son(String sonId, String sonName, Father father) {
this.sonId = sonId;
this.sonName = sonName;
this.father = father;
}
public Son() {
}
}
|
注意mappedBy和@JoinColumn的位置
更改测试:
1
2
3
4
| @Test
public void testDel() {
fatherRepository.deleteById("a");
}
|
执行的SQL:
1
2
3
4
5
| select father0_.id as id1_0_0_, father0_.name as name2_0_0_ from father father0_ where father0_.id=?
select sons0_.father_id as father_i3_1_0_, sons0_.son_id as son_id1_1_0_, sons0_.son_id as son_id1_1_1_, sons0_.father_id as father_i3_1_1_, sons0_.son_name as son_name2_1_1_ from son sons0_ where sons0_.father_id=?
delete from son where son_id=?
delete from son where son_id=?
delete from father where id=?
|
总结
- 级联删除新增不会新增关联对象
- 级联删除修改不会修改关联对象
- 级联删除删除会将所关联对象一并删除
REFRESH(级联刷新)
级联刷新,也就是说,当你刚开始获取到了这条记录,那么在你处理业务过程中,这条记录被另一个业务程序修改了(数据库这条记录被修改了),那么你获取的这条数据就不是最新的数据,那你就要调用实体管理器里面的refresh方法来刷新实体,所谓刷新,大家一定要记住方向,它是获取数据,相当于执行select语句的(但不能用select,select方法返回的是EntityManager缓存中的数据,不是数据库里面最新的数据),也就是重新获取数据。
DETACH(级联脱管/游离)
如果你要删除一个实体,但是它有外键无法删除,你就需要这个级联权限了。它会撤销所有相关的外键关联。
文章作者
itning
上次更新
2020年03月26日 12:36:32
许可协议
CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
